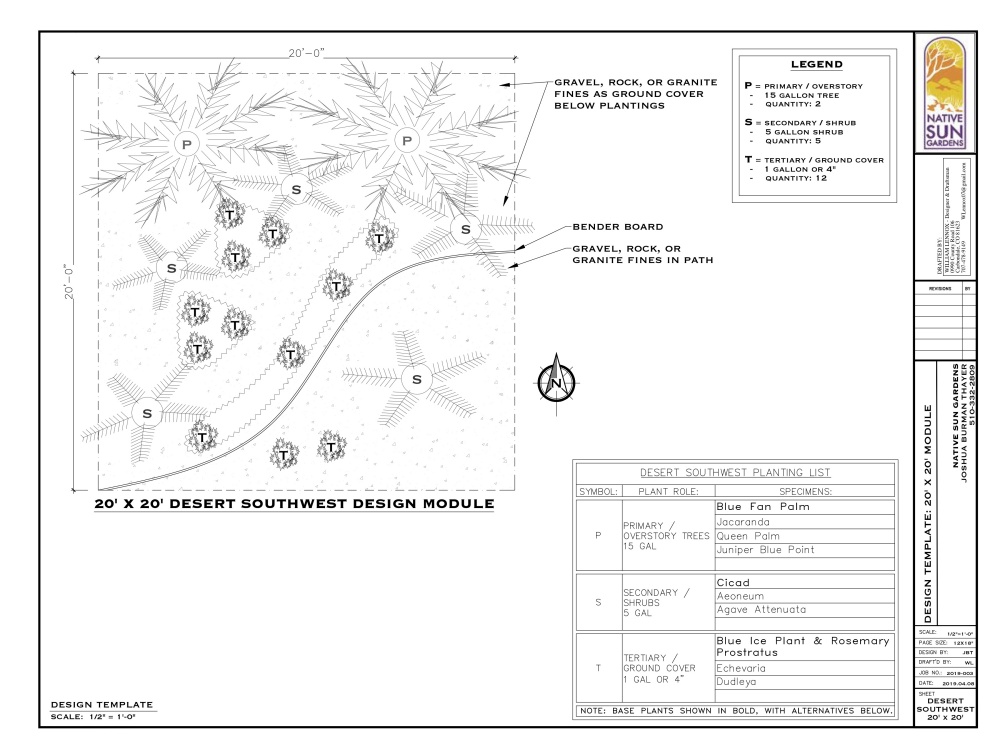
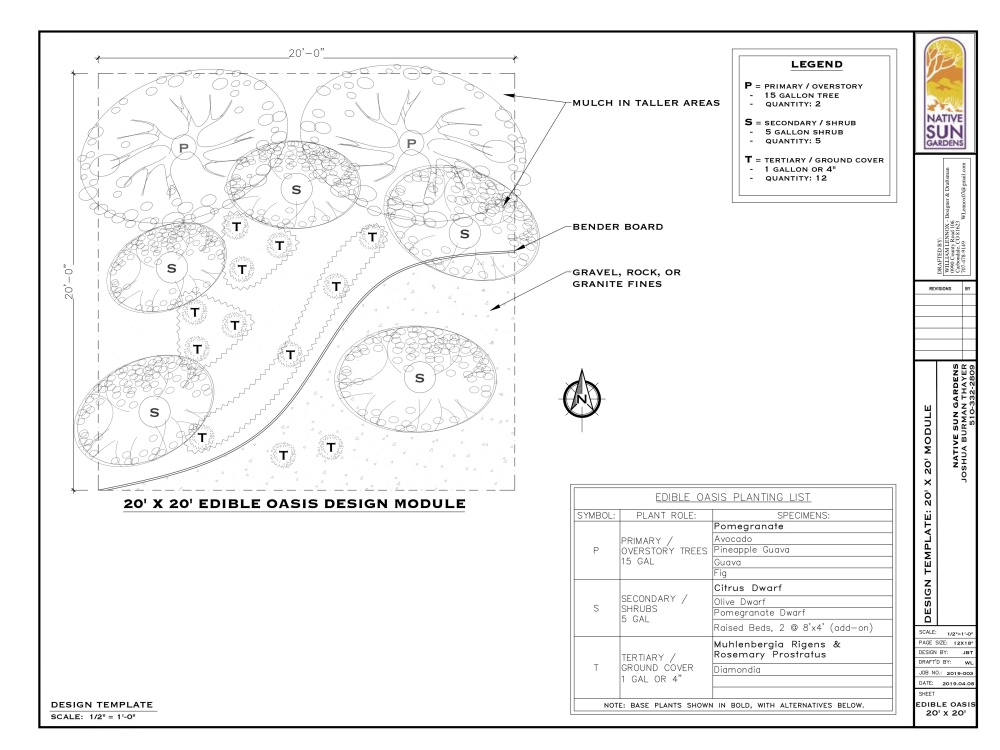
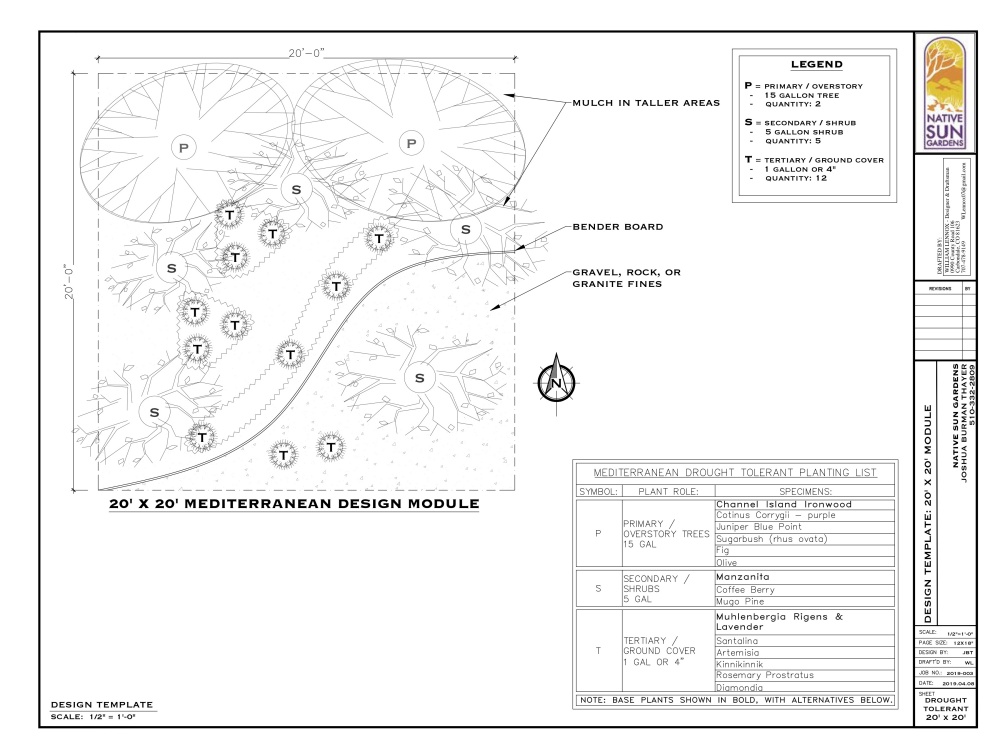
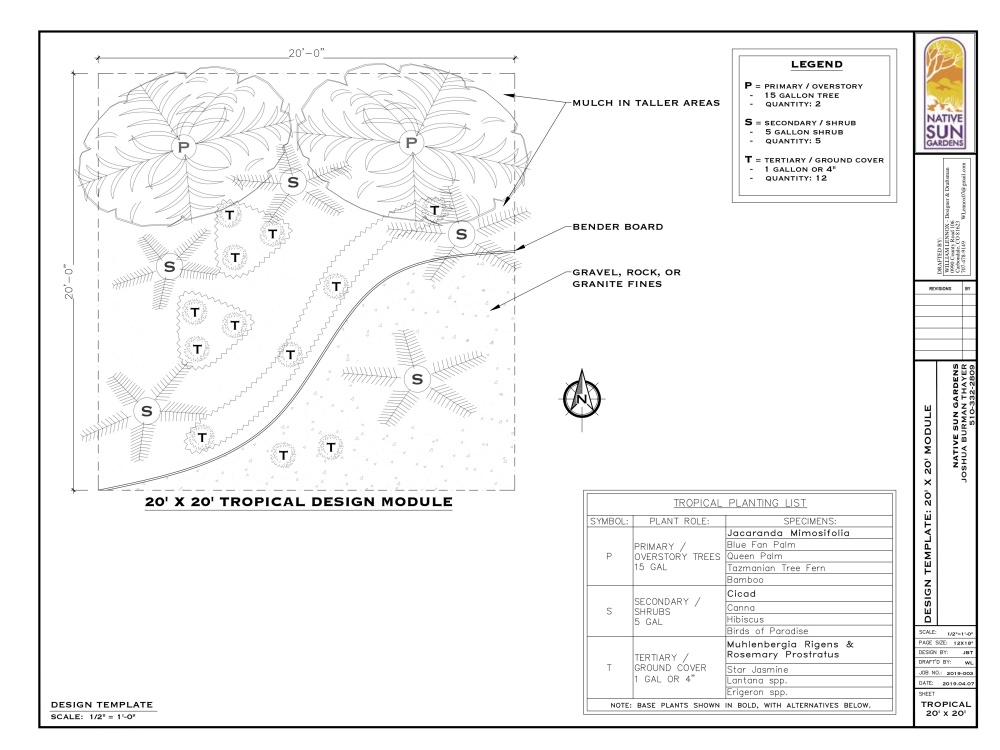
Testing Your Soil: A Toolkit for Gardeners
By Patrick Murphy, Program Manager
Soil testing is an accurate and definite way to get an idea about how your soil is doing and learn what issues you might be dealing with. But what type of tests are there? What information are you looking for? How do you determine which test is best? You may want to follow a “Learn. Test. Act.” approach. Learn about the site’s history, test your soil appropriately, and act upon the test results.
Learn about your future gardening location — The test you choose depends on the history of your site. Solano County was incorporated in 1850, and the county has seen a variety of industries come and go. As such, many possible urban agriculture sites lack a robust history. Do your research before you begin:
- What used to be near this garden space?
- What possible sources of contamination are there?
- What will you be growing?
You may wish to contact the local museum, or check out some online sources (see our toolkit for some suggestions) to learn more about your site’s history.
 Test your soil appropriately — A variety of tests are available to everyday people and many are fairly inexpensive. The most accessible type of test is probably a “nutrient panel” (often called a “soil paste” test), which gives you an idea of the nutrient content of your soil. This will give you a breakdown of each nutrient, soil pH, salinity, etc., depending on the lab and exact type of test. You can learn more about what needs to be addressed in your garden (e.g. a lack of nitrogen, too high a pH, etc.).
Test your soil appropriately — A variety of tests are available to everyday people and many are fairly inexpensive. The most accessible type of test is probably a “nutrient panel” (often called a “soil paste” test), which gives you an idea of the nutrient content of your soil. This will give you a breakdown of each nutrient, soil pH, salinity, etc., depending on the lab and exact type of test. You can learn more about what needs to be addressed in your garden (e.g. a lack of nitrogen, too high a pH, etc.).
The other common type of test would be some variety of heavy metal test. It is important to consider the variety of plants and produce you plan to harvest. Leafy vegetables (lettuce, kale, spinach) are known as hyperaccumulators and draw heavy metals up into their leaves. A key property of many leafy greens is their ability to accumulate heavy metals in their tissues without the traditional signs of toxicity. Do not assume plants will “reject” contamination; a significant number of plants humans consume can accumulate heavy metals in their edible areas. If you are concerned about heavy metals, such as lead and arsenic, you should test the soil you plan to grow in.
Primary Pollutant Metals-13 (“PPM-13”) and the California Administrative Manual-17 (“CAM-17”) are the standard tests to determine if you have heavy metals in your soil. PPM-13 looks for the 13 most common heavy metals, CAM-17 for the 17 most common. Either of these tests are perfect for locations where you believe there is a chance of heavy metal contamination. Additional tests exist to determine if soil has been contaminated with things like DDT, gasoline, etc. For more information about tests and costs, check out our soil contamination toolkit, or consult an environmental health specialist.
Act with the information you have — Once you have your results, decide what to do. You may have perfect soil that requires only that you begin planting. If you discover you do have a significant level of soil contamination in your garden space, you may want to consider alternative locations, remediation methods, or some combination of both. There are a number of good resources from agricultural offices and university extension programs, some are linked in our soil contamination toolkit. Always make sure the remediation technique you’re using is safe, effective, and observable. If you are attempting remediation, you will need to test your soil at regular intervals to evaluate how effective your efforts have been.
At Sustainable Solano, we have selected two potential sites that we plan to test over time to not only see what the soil composition looked like at the start of our work on these gardens, but also how our approach to building healthy soil and using permaculture practices affect the ongoing health of those gardens. We look forward to offering future updates on what this “Learn. Test. Act.” approach yields.

 Soil health is a big focus for Sustainable Solano this year. This March through May, we’ll be offering classes for all levels of composting to build healthy soil. This series will consist of three classes, with a beginners composting class in March, an intermediate class in April and an advanced composting class in May. You are invited to attend the class of your choice or join us for all three to build your composting knowledge and connect with the different gardens where each class will be held.
Soil health is a big focus for Sustainable Solano this year. This March through May, we’ll be offering classes for all levels of composting to build healthy soil. This series will consist of three classes, with a beginners composting class in March, an intermediate class in April and an advanced composting class in May. You are invited to attend the class of your choice or join us for all three to build your composting knowledge and connect with the different gardens where each class will be held. Composting 101 will be followed by Intermediate Compost Skills – An Introduction to Worm Composting, also taught by Lori Caldwell. This class will go over compost mishaps and how to troubleshoot bin repair, pests, etc. The time will also be used to introduce worm composting, discussing the benefits of worms, worm castings, and this compost method that is very friendly for those who want to compost but have less space to work with. The Vallejo Project Unity Garden will be hosting this class, with a worm bin and a three-bin compost system that has been paused due to pest issues and repair needs. This class will be interactive and potentially hands on, as we hope to show examples of bin repairs and give their compost system a bit of TLC.
Composting 101 will be followed by Intermediate Compost Skills – An Introduction to Worm Composting, also taught by Lori Caldwell. This class will go over compost mishaps and how to troubleshoot bin repair, pests, etc. The time will also be used to introduce worm composting, discussing the benefits of worms, worm castings, and this compost method that is very friendly for those who want to compost but have less space to work with. The Vallejo Project Unity Garden will be hosting this class, with a worm bin and a three-bin compost system that has been paused due to pest issues and repair needs. This class will be interactive and potentially hands on, as we hope to show examples of bin repairs and give their compost system a bit of TLC.